Aeroacoustic simulation of launch vehicle at lift-off
JAXA Supercomputer System Annual Report April 2019-March 2020
Report Number: R19EG3213
Subject Category: Research and Development
- Responsible Representative: Eiji Shima, Unit leader, Research Unit III, Research and Development Directorate
- Contact Information: tsutsumi.seiji@jaxa.jp(tsutsumi.seiji@jaxa.jp)
- Members: Ryoji Takaki, Seiji Tsutsumi, Hiroyuki Ito, Taro Shimizu, Junya Aono, Takanori Haga, Masaharu Abe, Kazuma Tago, Hiroshi Koizumi
Abstract
It is required to predict and reduce the acoustic level of satellites caused by exhaust jet of rocket engines and transonic buffet. In this study, the lift-off acousitc analysis tool developed so far is coupled with the FEM tool to predict the acoustic level inside payload fairing, aiming to develop quiet launch vehicle.
Reference URL
N/A
Reasons and benefits of using JAXA Supercomputer System
It is necessary to carry out billions of LES analysis, and large computing resources are essential to achieve the target frequency resolution.
Achievements of the Year
Aero-vibro acoustic simulation for the prediction of harmful acoustic loading at lift-off of launch vehicle is developed. In this simulation technique, high-fidelity large-eddy simulation with computational aeroacoutics based on full-Euler equations is employed for computing jet aeroacoustics and their propagation to the outside of payload fairing. Acoustic field inside the payload fairing is computed by the coupled vibro-acoustic simulation based on finite element method.
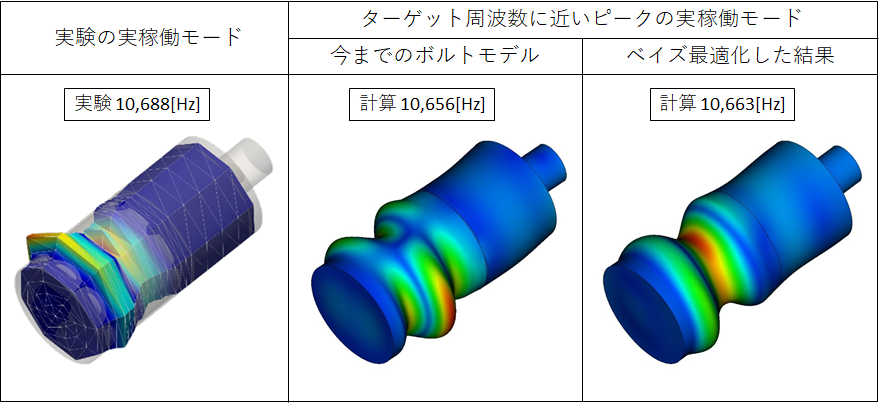
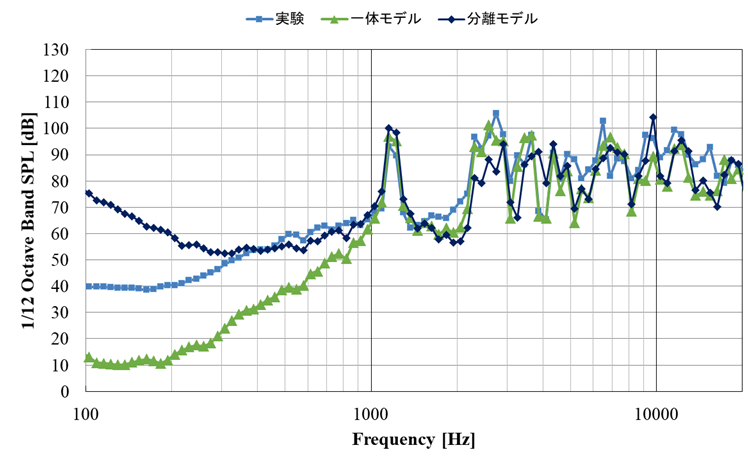
A simplified fairing model is used for the validation of the present method. An impact hammer test is conducted for validating the structural model in FEM analysis. Then, accuracy of the coupling method is validated by using the acoustic vibration test result with a subscale rocket engine. According to the result obtined last year, the bolt model of FEM had large impact on the mode shape of the simplified fairing model and the internal acoustic level. Therefore, the parameters of the bolt model were identified by the Bayesian optimization for the experimental modal analysis results.(Fig.1) Then, the accuracy of predicting internal acoustic environement was examined.(Fig.2)
Publications
N/A
Usage of JSS2
Computational Information
- Process Parallelization Methods: MPI
- Thread Parallelization Methods: OpenMP
- Number of Processes: 1
- Elapsed Time per Case: 700 Hour(s)
Resources Used
Fraction of Usage in Total Resources*1(%): 0.80
Details
Please refer to System Configuration of JSS2 for the system configuration and major specifications of JSS2.
| System Name | Amount of Core Time(core x hours) | Fraction of Usage*2(%) |
|---|---|---|
| SORA-MA | 6,602,380.65 | 0.80 |
| SORA-PP | 112,991.44 | 0.73 |
| SORA-LM | 3,071.42 | 1.28 |
| SORA-TPP | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| File System Name | Storage Assigned(GiB) | Fraction of Usage*2(%) |
|---|---|---|
| /home | 8,252.68 | 6.87 |
| /data | 39,807.28 | 0.68 |
| /ltmp | 5,776.75 | 0.49 |
| Archiver Name | Storage Used(TiB) | Fraction of Usage*2(%) |
|---|---|---|
| J-SPACE | 125.96 | 3.17 |
*1: Fraction of Usage in Total Resources: Weighted average of three resource types (Computing, File System, and Archiver).
*2: Fraction of Usage:Percentage of usage relative to each resource used in one year.
JAXA Supercomputer System Annual Report April 2019-March 2020