Computational Study on Aerodynamic Characteristics of Slender Body Configurations
JAXA Supercomputer System Annual Report April 2018-March 2019
Report Number: R18EACA12
Subject Category: JSS2 Inter-University Research
- Responsible Representative: Keiichi Kitamura, Associate Professor, Yokohama National University
- Contact Information: Yuya Takagi(takagi-yuuya-ks@ynu.jp)
- Members: Keiichi Kitamura, Yuya Takagi
Abstract
In this study, we attempted to improve the aerodynamic characteristics by attaching delta-wings and vortex-flaps to a slender body. Since the thickness of the fins is small, it is difficult to carry out the wind tunnel experiment. However, we succeeded in acquiring aerodynamic characterisitics and flow visualizations by numerical analysis. In the future, it is a goal to study better aerodynamic devices such as the shape of fins.
Reference URL
N/A
Reasons for using JSS2
Goal
We clarify the mechanism by which aerodynamic device affects a slender body, and we propose an excellent shape.
Necessity
According to the previous studies, in order to resolve vortices generated around the body and fins, it is known that the unsteady calculation needs at least 30 million elements. Therefore, we used JSS2 so as to reduce computational time.
Use
Since it was necessary to reduce the computational time for large-scale calculation, we used JSS2.
Achievements of the Year
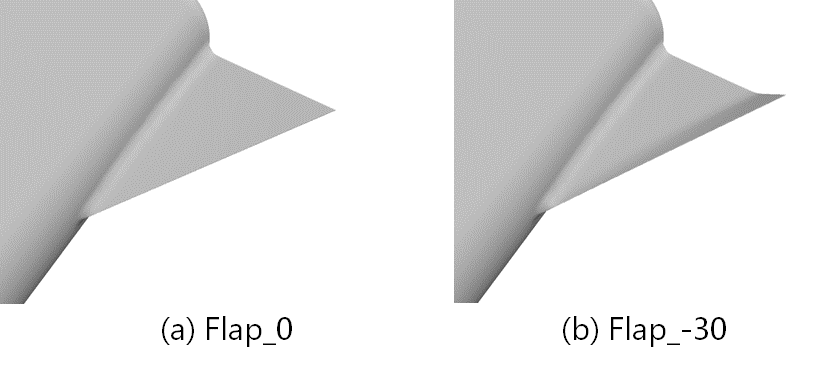
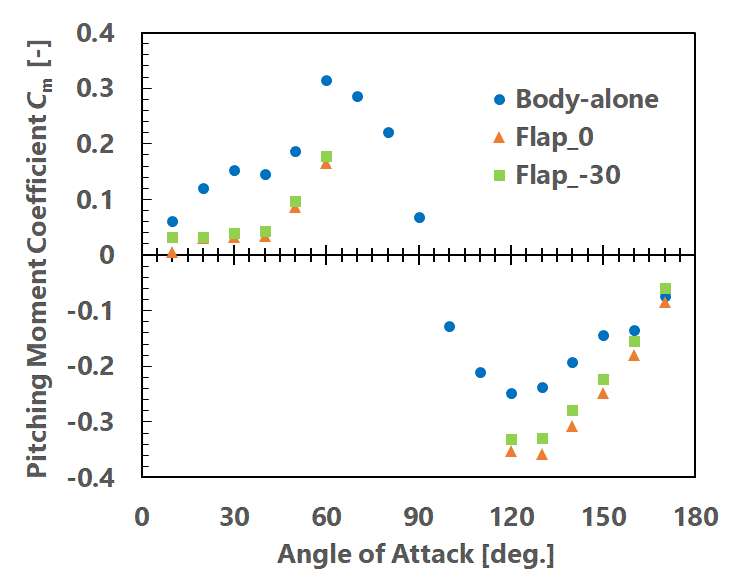
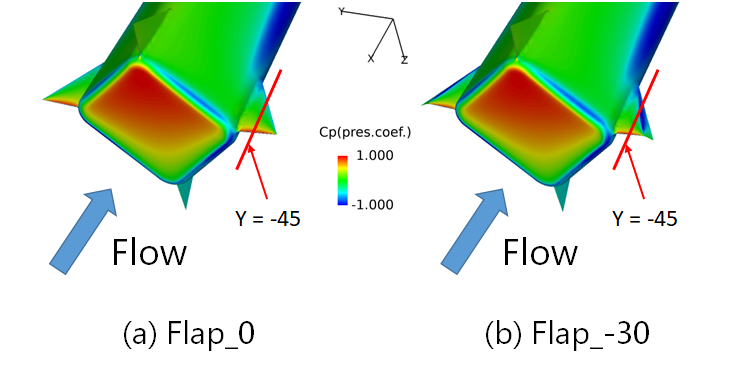
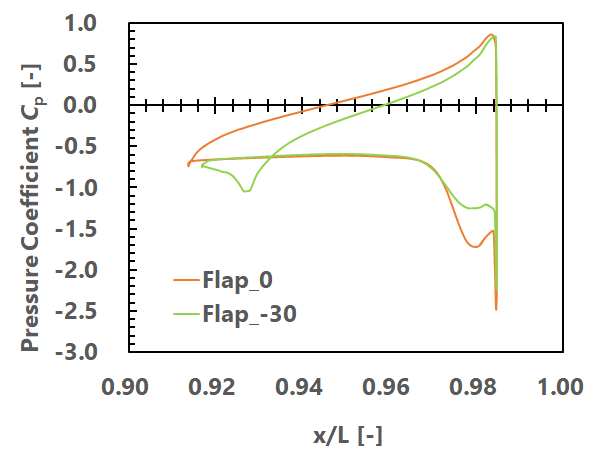
We attached delta-wings and vortex-flaps on a slender body, and acquired an aerodynamic coefficient and visualize a flow field. Fig. 1 shows the fin shapes. We calculated three cases and we calld the case of only body as Body-alone, the case of not deflected fins as Flap _ 0, and the case of the flap deflacted by -30 degrees as Flap_-30, respectively. Fig. 2 shows Cm characteristics. Comparing Body-alone and Flap_0, Flap_0 was totally able to reduce Cm, however absolute value increased at the backward angles (angles of attack from 90 degrees to 180 degrees). Therefore, comparing Flap_0 and Flap_-30 in the backward angles, Flap_-30 can reduce the absolute value because, by deflecting flaps, the pressure difference between upper and lower surface of the fins became smaller and then the normal force became smaller (Fig. 3 and 4).
Publications
– Oral Presentations
Takagi, Y., Aogaki, T., Kitamura, K., and Nonaka, S.: Numerical Study on Aerodynamic Improvement of Slender-bodied Reusable Rocket by Fins and Vortex Flaps, 15th International Space Conference of Pacific-basin Societies, Montreal, Canada, 2018.
Usage of JSS2
Computational Information
- Process Parallelization Methods: MPI
- Thread Parallelization Methods: N/A
- Number of Processes: 512 – 1024
- Elapsed Time per Case: 100 Hour(s)
Resources Used
Fraction of Usage in Total Resources*1(%): 0.28
Details
Please refer to System Configuration of JSS2 for the system configuration and major specifications of JSS2.
| System Name | Amount of Core Time(core x hours) | Fraction of Usage*2(%) |
|---|---|---|
| SORA-MA | 2,289,004.68 | 0.28 |
| SORA-PP | 20,758.14 | 0.17 |
| SORA-LM | 13,224.09 | 6.17 |
| SORA-TPP | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| File System Name | Storage Assigned(GiB) | Fraction of Usage*2(%) |
|---|---|---|
| /home | 25.75 | 0.03 |
| /data | 4,901.89 | 0.09 |
| /ltmp | 1,367.19 | 0.12 |
| Archiver Name | Storage Used(TiB) | Fraction of Usage*2(%) |
|---|---|---|
| J-SPACE | 1.22 | 0.04 |
*1: Fraction of Usage in Total Resources: Weighted average of three resource types (Computing, File System, and Archiver).
*2: Fraction of Usage:Percentage of usage relative to each resource used in one year.
JAXA Supercomputer System Annual Report April 2018-March 2019