Numerical Simulations of Fully Developed Turbulence
JAXA Supercomputer System Annual Report April 2018-March 2019
Report Number: R18EACA05
Subject Category: JSS2 Inter-University Research
- Responsible Representative: Susumu Goto, Professor, Osaka University
- Contact Information: Susumu Goto(goto@me.es.osaka-u.ac.jp)
- Members: Susumu Goto, Jun Kanki, Yutaro Motoori, Toru Kubo, Tomoyuki Kurita, Ryo Araki, Tsukasa Shinohara
Abstract
Flows in various systems appearing in the aerospace engineering are fully developed turbulence at high Reynolds numbers. To numerically simulate these flows, we usually need to model small-scale motions in the flow. Such turbulence models are on the basis of classical theories of small-scale statistics of turbulence. However, recent laboratory experiments and numerical simulations showed that these classical theories did not necessarily hold (Goto & Vassilicos 2015, 2016). The main aim of the present study is to reveal (un)universality of small-scale statistics and physics behind it by means of direct numerical simulations of turbulence under various boundary conditions.
Reference URL
N/A
Reasons for using JSS2
Turbulent flows are one of the most important topics in the field of aerospace engineering. The direct numerical simulations of fully developed turbulence require a massively parallel supercomputer with sufficient amount of memories and storages. These are the reasons to use JSS2.
Achievements of the Year
In this year, we revealed important knowledge on the sustaining mechanism of developed turbulence in a rotating container. It is well-known that strong turbulence is sustained in a rotating container when its spin axis weakly precesses. We have developed a numerical code with a flexible grid generation method to conduct simulations of flow in an arbitrary-shaped container. We have conducted simulations of turbulence in a precessing sphere, spheroids, and a cylinder and investigated the sustainability condition and mechanism of developed turbulence. Irrespective of the container’s shape, strong turbulence is sustained when the precession is relatively weak, and it is always accompanied by a pair of large-scale twisted vortices (Fig. 1).
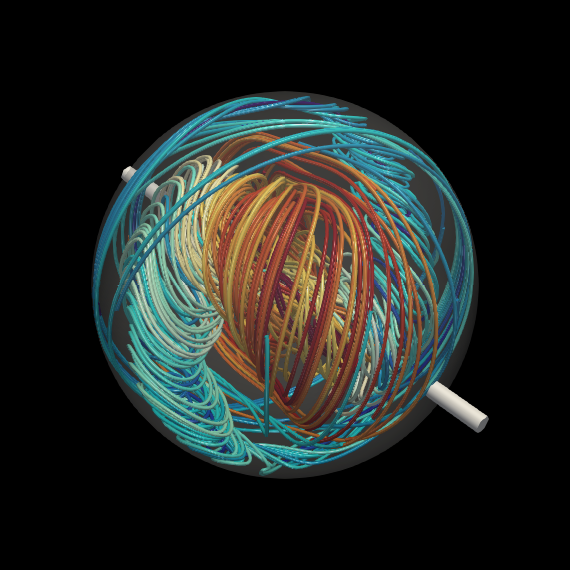
Fig.1: Streamlines of the mean flow of developed turbulence sustained in a precessing sphere. The direction of the velocity is from red to blue. Developed turbulence driven by precession is, irrespective of the container’s shape, accompanied by a similar pair of large-scale vortices.
Publications
– Peer-reviewed papers
1) K. Komoda and S. Goto, Three-dimensional flow structures of turbulence in precessing spheroids, Phys. Rev. Fluids 4 (2019) 014603.
2) Y. Motoori and S. Goto, Generation mechanism of a hierarchy of vortices in a turbulent boundary layer, J. Fluid Mech., 865 (2019) 1085-1109.
– Invited Presentations
1) S. Goto, Energy cascade in turbulence, Workshop on Fluid turbulence and Singularities of the Euler/Navier Stokes equations, Harvard Univ. 13 March 2019.
– Oral Presentations
1) Y. Motoori and S. Goto, Hierarchy of vortices in wall-bounded turbulence, The 15th International Conference on Flow Dynamics.
2) S. Goto, Coherent structures in turbulence and their universality, International Conference on APEF 2018 (Advances in Physics of Emergent Orders in Fluctuations).
Usage of JSS2
Computational Information
- Process Parallelization Methods: MPI
- Thread Parallelization Methods: Automatic Parallelization
- Number of Processes: 64 – 96
- Elapsed Time per Case: 35 Hour(s)
Resources Used
Fraction of Usage in Total Resources*1(%): 0.18
Details
Please refer to System Configuration of JSS2 for the system configuration and major specifications of JSS2.
| System Name | Amount of Core Time(core x hours) | Fraction of Usage*2(%) |
|---|---|---|
| SORA-MA | 1,205,735.81 | 0.15 |
| SORA-PP | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| SORA-LM | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| SORA-TPP | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| File System Name | Storage Assigned(GiB) | Fraction of Usage*2(%) |
|---|---|---|
| /home | 561.71 | 0.58 |
| /data | 64,048.80 | 1.13 |
| /ltmp | 14,648.44 | 1.25 |
| Archiver Name | Storage Used(TiB) | Fraction of Usage*2(%) |
|---|---|---|
| J-SPACE | 0.00 | 0.00 |
*1: Fraction of Usage in Total Resources: Weighted average of three resource types (Computing, File System, and Archiver).
*2: Fraction of Usage:Percentage of usage relative to each resource used in one year.
JAXA Supercomputer System Annual Report April 2018-March 2019