Study of scale effects on the atmospheric entry environment of atmospheric entry capsules
JAXA Supercomputer System Annual Report February 2023-January 2024
Report Number: R23EDA201J04
Subject Category: Aeronautical Technology
- Responsible Representative: Toshiya Nakamurai, Aviation Technology Directrate, Fundamental Aeronautics Research Unit
- Contact Information: Shingo Matsuyama(matsuyama.shingo@jaxa.jp)
- Members: Shingo Matsuyama, Ryotaro Murakami, Kasumi Nakura
Abstract
It is known that aerodynamic heating rate, real gas aerodynamic characteristics, and static and dynamic instabilities, which are important prerequisites for the design of atmospheric entry systems, change significantly with changes in capsule shape, but they also change with different representative lengths (scales), even for similar shapes. However, there is no quantitative correlation known to what extent changes in scale affect these properties, so it is necessary to predict them at each design stage. The objective of this study is to develop a numerical method to predict scale effects for a 3/5 scale capsule of HTV Small Re-entry Capsule (HSRC) and to validate this method by comparing it with flight data.
Reference URL
N/A
Reasons and benefits of using JAXA Supercomputer System
In this study, three-dimensional analyses are performed for an atmospheric entry capsule flying at an angle of attack, so a large computational cost is inevitable. In addition, since turbulence analysis by Large Eddy Simulation (LES) is the main method for evaluating dynamic instability in transonic speeds, a large-scale three-dimensional unsteady analysis is inevitably required. In addition, for flight conditions exceeding Mach 10, the governing equations for a large number of chemical species and internal energies must be solved because chemical reactions and excitation of internal energy modes occur behind the shock wave. These analyses are computationally very expensive and require the use of a supercomputer.
Achievements of the Year
-CFD analyses were performed on the capsule geometry with the HSRC scaled down to 3/5 scale to evaluate the aerodynamic heating and dynamic instability characteristics.
-The aerodynamic characteristics of the capsule and the heat flux distribution on the wall for the peak heating condition were obtained by evaluating the flow field around the capsule at Mach 22 by three-dimensional steady-state analysis (Figure 1).
-Three-dimensional unsteady LES was performed at Mach 1.2 for the flight condition just before parachute deployment to evaluate the unsteady aerodynamic characteristics of the capsule (Figure 2).
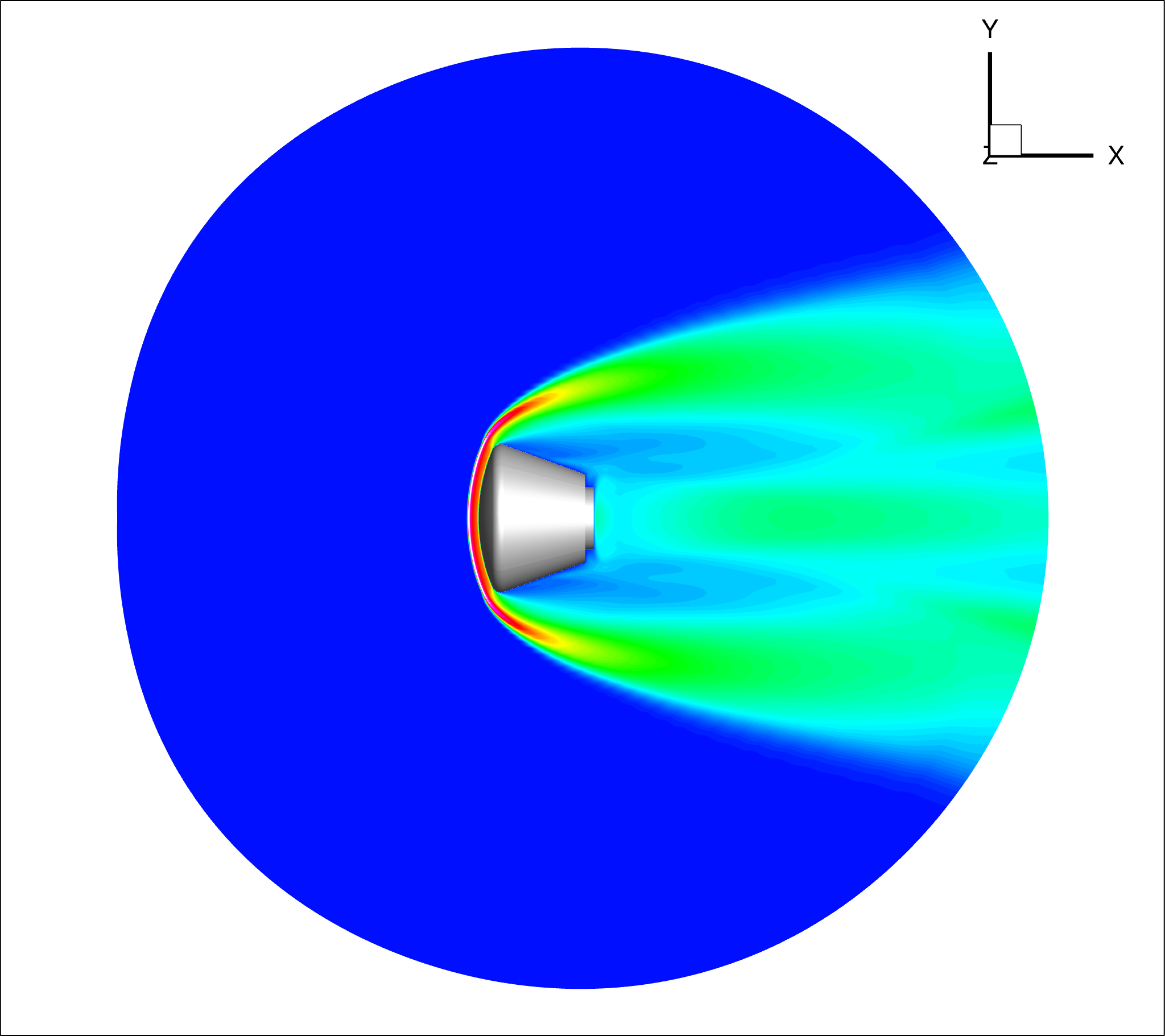
Fig.1: Flow field around a capsule flying at Mach 22. Result of translational temperature distribution by a three-dimensional steady-state analysis is shown.
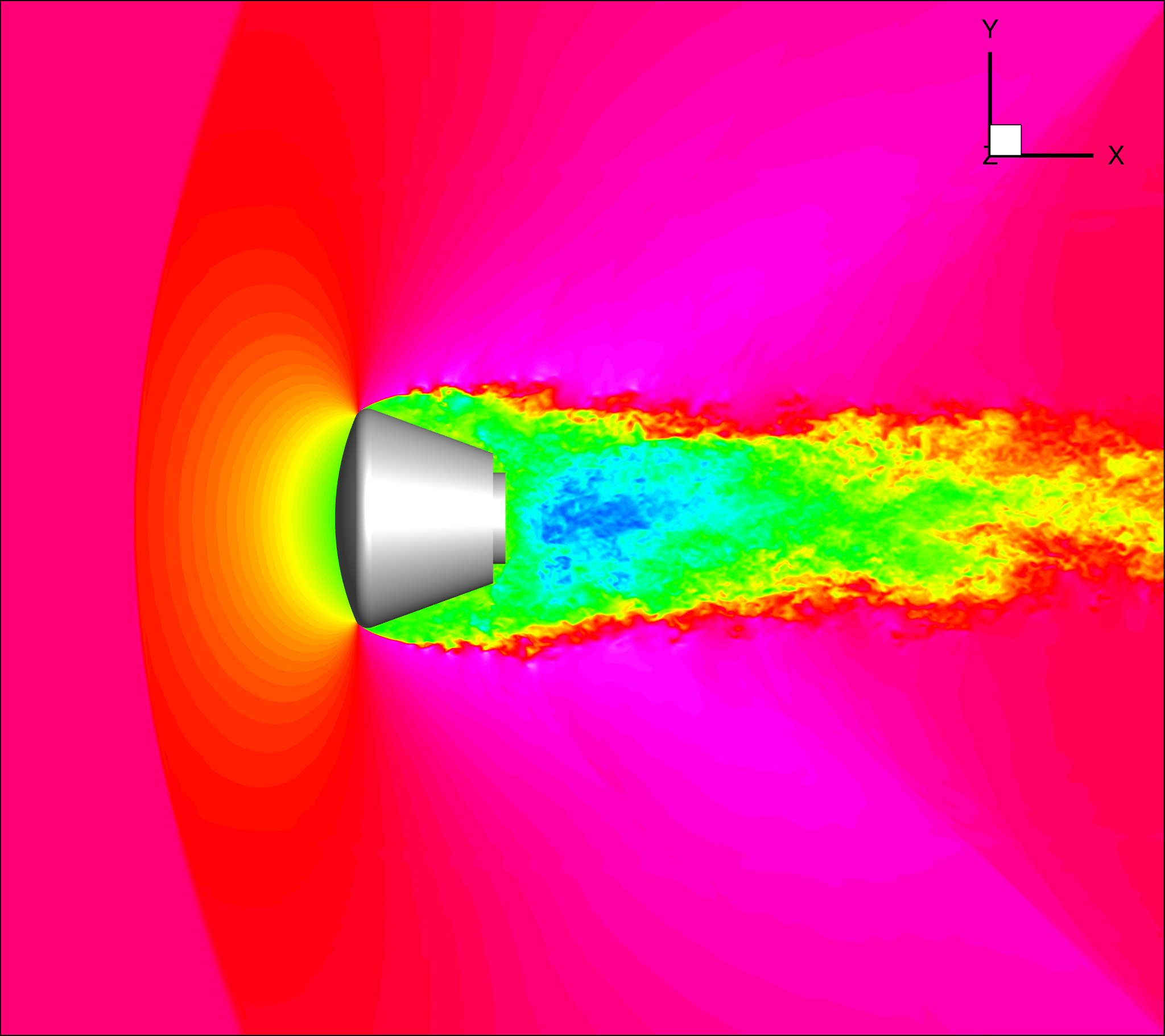
Fig.2: Flow field around a capsule flying at Mach 1.2. Result of instantaneous velocity distribution by a three-dimensional unsteady LES is shown.
Publications
N/A
Usage of JSS
Computational Information
- Process Parallelization Methods: MPI
- Thread Parallelization Methods: OpenMP
- Number of Processes: 52 – 2788
- Elapsed Time per Case: 100 Hour(s)
JSS3 Resources Used
Fraction of Usage in Total Resources*1(%): 0.24
Details
Please refer to System Configuration of JSS3 for the system configuration and major specifications of JSS3.
| System Name | CPU Resources Used(Core x Hours) | Fraction of Usage*2(%) |
|---|---|---|
| TOKI-SORA | 6598216.64 | 0.30 |
| TOKI-ST | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| TOKI-GP | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| TOKI-XM | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| TOKI-LM | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| TOKI-TST | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| TOKI-TGP | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| TOKI-TLM | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| File System Name | Storage Assigned(GiB) | Fraction of Usage*2(%) |
|---|---|---|
| /home | 28.82 | 0.02 |
| /data and /data2 | 1801.18 | 0.01 |
| /ssd | 295.30 | 0.03 |
| Archiver Name | Storage Used(TiB) | Fraction of Usage*2(%) |
|---|---|---|
| J-SPACE | 0.39 | 0.00 |
*1: Fraction of Usage in Total Resources: Weighted average of three resource types (Computing, File System, and Archiver).
*2: Fraction of Usage:Percentage of usage relative to each resource used in one year.
ISV Software Licenses Used
| ISV Software Licenses Used(Hours) | Fraction of Usage*2(%) | |
|---|---|---|
| ISV Software Licenses(Total) | 0.00 | 0.00 |
*2: Fraction of Usage:Percentage of usage relative to each resource used in one year.
JAXA Supercomputer System Annual Report February 2023-January 2024