Feedback Control of Flow Separation Using DBD Plasma Actuator
JAXA Supercomputer System Annual Report April 2016-March 2017
Report Number: R16E0060
- Responsible Representative: Kengo Asada(Tokyo University of Science)
- Contact Information: Kengo Asada(asada@rs.tus.ac.jp)
- Members: Kengo Asada, Takuto Ogawa
- Subject Category: Aviation(Aircraft,Body sound,Aircraft engine)
Abstract
The project develops flow control technic by using dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma actuator to establish high efficient and robust vehicle systems such as rockets, aircrafts, and motor vehicles. We propose and demonstrate feedback control methods to adapt unsteady flows over the vehicles through a series of high-fidelity unsteady simulations.
Goal
The project aims at developments of low-cost and robust vehicles which involves unsteady flows such as aircrafts, rockets, and turbo engines by the establishment of active flow control technology.
Objective
The project proposes and demonstrates feedback control methods for unsteady active flow control through a series of high-fidelity large-eddy simulations.
References and Links
N/A
Use of the Supercomputer
High-fidelity 3D unsteady simulations (large-eddy simulations, LES) with the LANS3D which is a compressible Navier-Stokes solver are performed to demonstrate and improve the feedback flow control method whose effectiveness was confirmed by 2D simulations.
Necessity of the Supercomputer
Computational speed of general-purpose computers is not sufficient to conduct high-fidelity LES.
Achievements of the Year
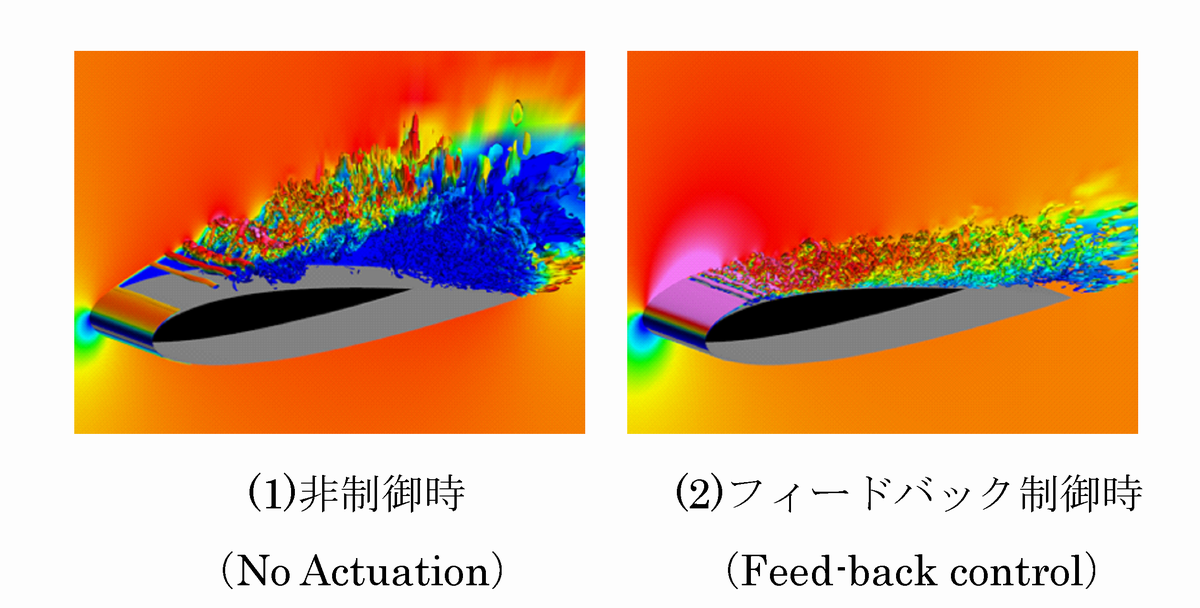
High-fidelity LESs of the NACA0015 airfoil flow controlled by a DBD plasma actuator with a feedback control law whose effectiveness is confirmed by 2D simulations. The present feedback law drives the actuator located at 5% of the chord length from the leading edge when a surface pressure measured at 40% of the chord length from the leading edge rapidly decrease. The rapid decrease of pressure is assumed as an index of passing vortex in the present feedback control law. Figure 1 shows the time variation of the pressure coefficient (Cp), the moving average of Cp, and the state of actuation (ON/OFF). The figure shows that the actuator is intermittently driven depending on the pressure variation. The intermittent actuation is known as an effective operation of the DBD plasma actuator. The present control law succeeds to lead such an intermittent actuation. Figure 2 shows the vortex structures by iso-surface of Q-criterion colored by chordwise velocity. The figure indicates that the present feed-back controlsuppresses the separated region.
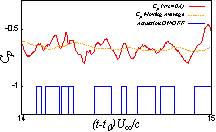
Fig.1:Time variation of the pressure coefficient (Cp), the moving average of Cp, and the state of actuation
Publications
N/A
Computational Information
- Parallelization Methods: Hybrid Parallelization
- Process Parallelization Methods: MPI
- Thread Parallelization Methods: OpenMP,Automatic Parallelization
- Number of Processes: 76
- Number of Threads per Process: 32
- Number of Nodes Used: 76
- Elapsed Time per Case (Hours): 25
- Number of Cases: 9
Resources Used
Total Amount of Virtual Cost(Yen): 642,211
Breakdown List by Resources
| System Name | Amount of Core Time(core x hours) | Virtual Cost(Yen) |
|---|---|---|
| SORA-MA | 391,455.18 | 621,167 |
| SORA-PP | 0.00 | 0 |
| SORA-LM | 0.00 | 0 |
| SORA-TPP | 0.00 | 0 |
| File System Name | Storage assigned(GiB) | Virtual Cost(Yen) |
|---|---|---|
| /home | 19.07 | 74 |
| /data | 1,428.69 | 5,615 |
| /ltmp | 3,906.25 | 15,353 |
| Archiving System Name | Storage used(TiB) | Virtual Cost(Yen) |
|---|---|---|
| J-SPACE | 0.00 | 0 |
Note: Virtual Cost=amount of cost, using the unit price list of JAXA Facility Utilization program(2016)
JAXA Supercomputer System Annual Report April 2016-March 2017