Study of particle Mach number and temperature effects on shock-particle interaction
JAXA Supercomputer System Annual Report February 2024-January 2025
Report Number: R24EACA55
Subject Category: JSS Inter-University Research
- Responsible Representative: Takayuki Nagata, Assistant Professor, Nagoya University
- Contact Information: Takayuki Nagata (Assistant Professor at Nagoya University)(takayuki.nagata@mae.nagoya-u.ac.jp)
- Members: Taku Nonomura, Takayuki Nagata
Abstract
Compressible flow around particles placed in a flowfield is investigated by the direct numerical simulation of the Navier-Stokes equations at Reynolds number of O(10^2). The objective of the present study is to obtained fundamental insight into the effects of aerodynamic interference between particles in subsonic to supersonic flows. Influences of the aerodynamic interference on the lift, drag, and moment coefficients of the particles are determined, and the flow physics is investigated based on detailed information such as velocity and pressure distributions. The calculation condition is designed for conditions in which particles in a high-speed flow pass through shock waves, turbulence, and shear layer. In addition to the knowledge of high-speed flow around single particles obtained in our previous research, the aerodynamic interference between particles will be clarified to obtain fundamental knowledge for the high-fidelity modeling of compressible gas-particle flows.
Reference URL
N/A
Reasons and benefits of using JAXA Supercomputer System
In the present study, a parametric study by direct numerical simuation of the Navier-Stokes equations is conducted, and thus, a large-scale parallel calculation is required.
Achievements of the Year
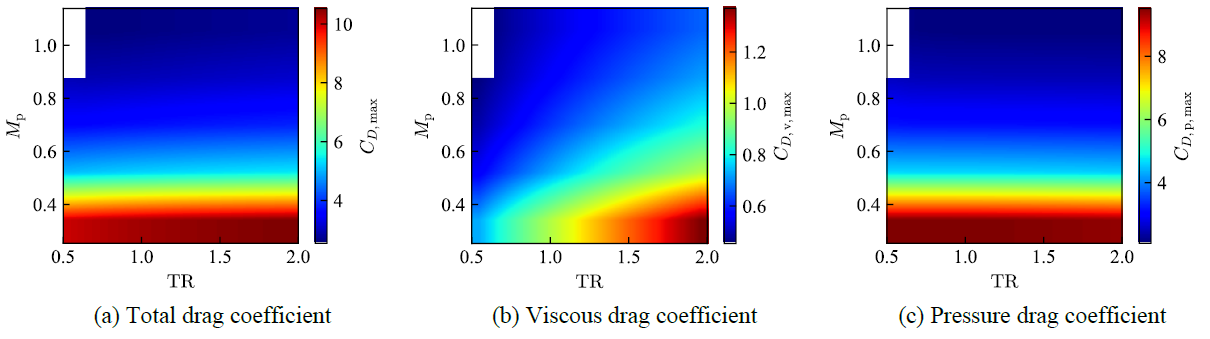
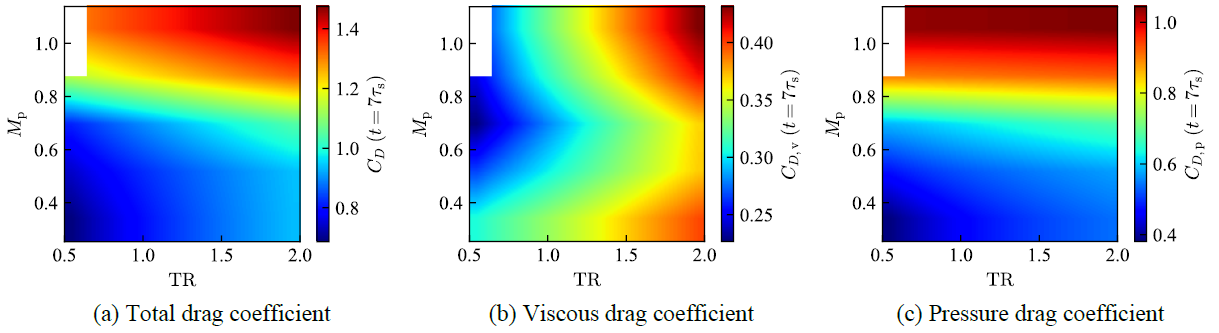
The particle temperature and Mach number effects on drag coefficient in the shock-particle interaction process were investigated by direct numerical simulations and axisymmetric simulations of compressible Navier–Stokes equations. The particle Reynolds number was set to 300, and the particle Mach number and the particle temperature were varied. The isothermal condition or adiabatic condition was imposed on the particle surface. The results of three-dimensional simulations showed that the axial symmetry of flow field is preserved at least until t=7t_s. The drag coefficient obtained by the axisymmetric and three-dimensional simulations was approximately equal at least until t=7t_s. Influences of the particle temperature and the particle Mach number on the drag coefficient were elucidated by axisymmetric simulations under various conditions.
Publications
N/A
Usage of JSS
Computational Information
- Process Parallelization Methods: MPI
- Thread Parallelization Methods: OpenMP
- Number of Processes: 1 - 324
- Elapsed Time per Case: 20 Hour(s)
JSS3 Resources Used
Fraction of Usage in Total Resources*1(%): 0.04
Details
Please refer to System Configuration of JSS3 for the system configuration and major specifications of JSS3.
| System Name | CPU Resources Used(Core x Hours) | Fraction of Usage*2(%) |
|---|---|---|
| TOKI-SORA | 1018753.07 | 0.05 |
| TOKI-ST | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| TOKI-GP | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| TOKI-XM | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| TOKI-LM | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| TOKI-TST | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| TOKI-TGP | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| TOKI-TLM | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| File System Name | Storage Assigned(GiB) | Fraction of Usage*2(%) |
|---|---|---|
| /home | 54.45 | 0.04 |
| /data and /data2 | 9526.22 | 0.05 |
| /ssd | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Archiver Name | Storage Used(TiB) | Fraction of Usage*2(%) |
|---|---|---|
| J-SPACE | 17.95 | 0.06 |
*1: Fraction of Usage in Total Resources: Weighted average of three resource types (Computing, File System, and Archiver).
*2: Fraction of Usage:Percentage of usage relative to each resource used in one year.
ISV Software Licenses Used
| ISV Software Licenses Used(Hours) | Fraction of Usage*2(%) | |
|---|---|---|
| ISV Software Licenses(Total) | 0.00 | 0.00 |
*2: Fraction of Usage:Percentage of usage relative to each resource used in one year.
JAXA Supercomputer System Annual Report February 2024-January 2025